 REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
 REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
 REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
REFORMS IMPLEMENTED
Department of Justice (DoJ) in collaboration with the eCommittee of the Supreme Court and with the active assistance of the High Courts of Delhi, Bombay, Karnataka and Calcutta has spearheaded various reforms to provide conducive environment for speedy resolution of commercial disputes.
Establishment of Dedicated Commercial Courts with pecuniary jurisdiction upto Rs 3 lakh, online e-filing, e-payment of court fees, electronic service of processes, random and automated allocation of cases including removal of manual checkbox system; institutionalization of Case Management Hearing and Pre-Trial Conference besides widespread use of Electronic Case Management Hearing Tools by Judges and Lawyers has improved the efficiency and efficacy of Dedicated Commercial Courts which has improved the business climate in India thereby reducing the time taken for trial and judgment in these courts.
| DBR: 2020 | Present Status | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indicators | Delhi | Mumbai | Delhi | Mumbai |
| Time-Days | 1445 | 1445 | 744 | 626 |
| Filing and Service | 45 | 45 | 15 | 15 |
| Trial and Judgment | 1095 | 1095 | 424 | 306 |
| Enforcement of Judgment | 305 | 305 | 305 | 305 |
As per Section 35 of Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 as amended in the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 the attorney fees and court fees is payable by unsuccessful party to the successful party. The Commercial courts are empowered to award compensatory costs for false and vexatious claims (Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 as amended in the Commercial Courts Act, 2015).
The Doing Business Report 2020 indicates cost (31 % of claim value) for India (both in Delhi and Mumbai) as -
a) Attorney Fees – 22%
b) Court Fees – 8.5%
c) Enforcement Fees – 0.5%
d) Expert fee – No fixed amount payable to ‘expert witness’ as per Order XVI Rule 2 (4) the CPC, Section 45 of the Indian Evidence Act as well as the High Court of Delhi/Bombay Rules. Commercial Court stands authorised to allow reasonable remuneration to an ‘expert witness’.
The High Courts of Delhi and Bombay issued circulars to the Commercial Courts to follow the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 as amended in the Commercial Court Act, 2015 in respect of all commercial disputes.
Committee on Simplification of Rules and Forms
The Department of Justice has constituted a Committee to work on the simplification of rules and forms in context of the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 and to examine the overall functioning of the Pre-Institution Mediation and Settlement mechanism including rationalization of Mediation fees to reduce compliance burden for citizens and businesses.
The Committee has finalised the Draft Commercial Court Rules, 2021 as per Section 21 A of the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 and the same is under examination of the Department of Legal Affairs.
Automatic and Random Allocation of Commercial Cases
The Commercial Cases are randomly and automatically assigned to the Dedicated Commercial Courts of Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru and Kolkata using Case Information System (CIS 3.2) software. This digital and automated system has eliminated human intervention in case allocation and created a faceless, transparent and credible method for case assignment.
Click Here for Presentation on working of Random Allocation of Commercial Cases

a) Delhi:
• The automatic and random allocation of commercial cases using CIS 3.2 software was introduced on 15.02.2019.
• Further, since 20.03.2020, the check box has been removed and any human intervention has been eliminated.
b) Mumbai:
• The automatic and random allocation of commercial cases using CIS 3.2 software was introduced on 13.02.2019.
• Further, since May, 2020, the check box system has been removed.
a) Time Standards:
• Code of Civil Procedure, 1908, Order XV-A, which was introduced through the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 for commercial disputes of specified value, outlines how case management or pre-trial conference is to be conducted. It provides for scheduling of timelines throughout the life cycle of a suit.
• Time standards are respected in more than 50% of cases in Dedicated Commercial Courts. Fixing of time standards for key court events and streamlining of trial process has led to speeding up case disposal, thus benefitting both litigants as well as lawyers.
b) Rules on Adjournments:
• Order XVII Rule (1) CPC provides for a maximum of three adjournments during the hearing of a suit.
• Order XVII, Rule 2(b) CPC states that no adjournment shall be granted at the request of a party, except where the circumstances are beyond the control of the parties.
• Department of Justice sent letter to High Courts of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka to adhere to the three adjournment rule. Pursuant to which, the four High Courts have issued advisory to all the Dedicated Commercial Courts under their jurisdiction to strictly adhere to the timelines and three adjournment rule.
• Maximum three adjournment rule is being actively enforced in more than 50% of cases of Dedicated Commercial Courts of Delhi, Mumbai, Kolkata and Bengaluru. This has reduced the time taken for trial, arguments and final judgment.
e-Committee, Supreme Court has ensured compliance of three adjournment rule by creating a facility which is provided in "daily proceedings screen" to alert judges about listing of cases.
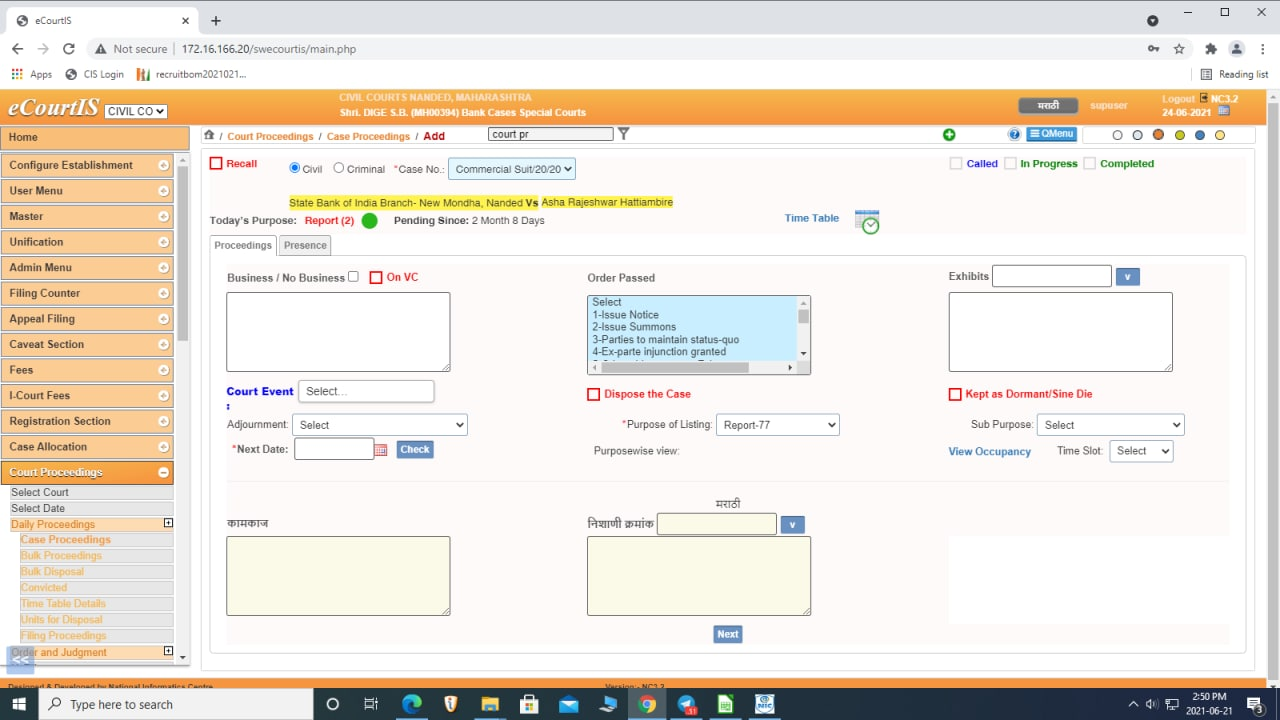
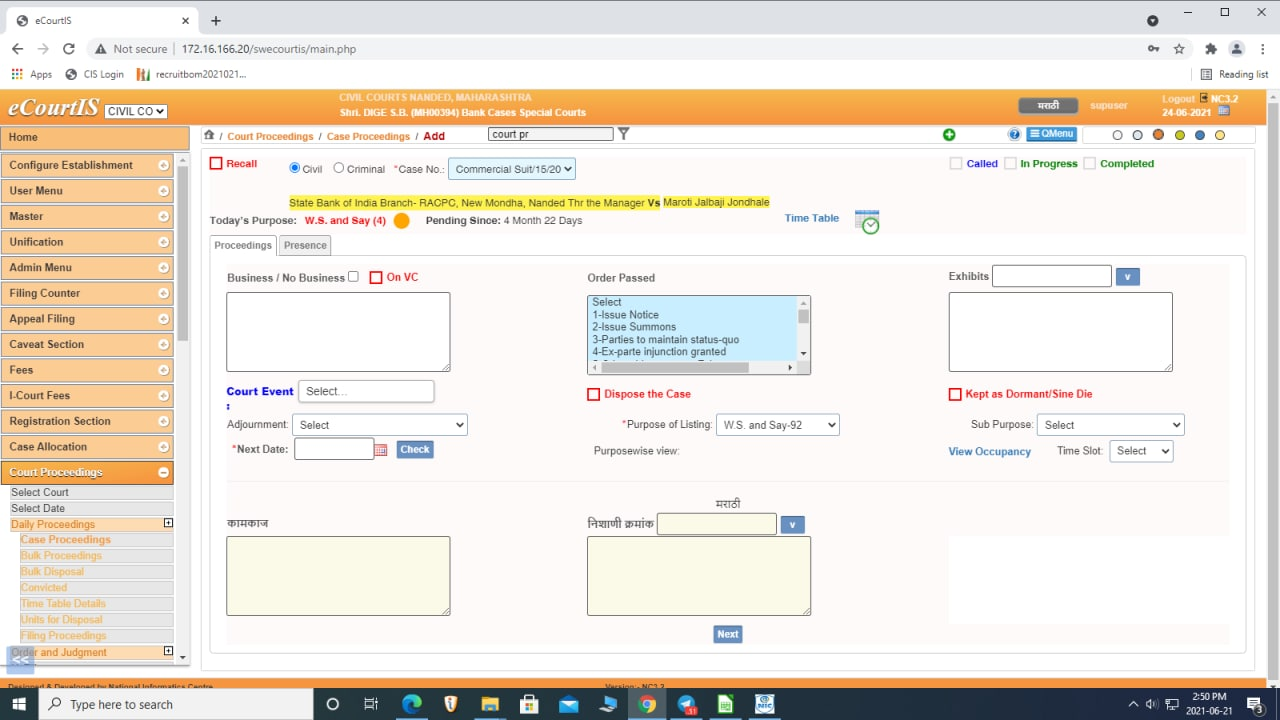
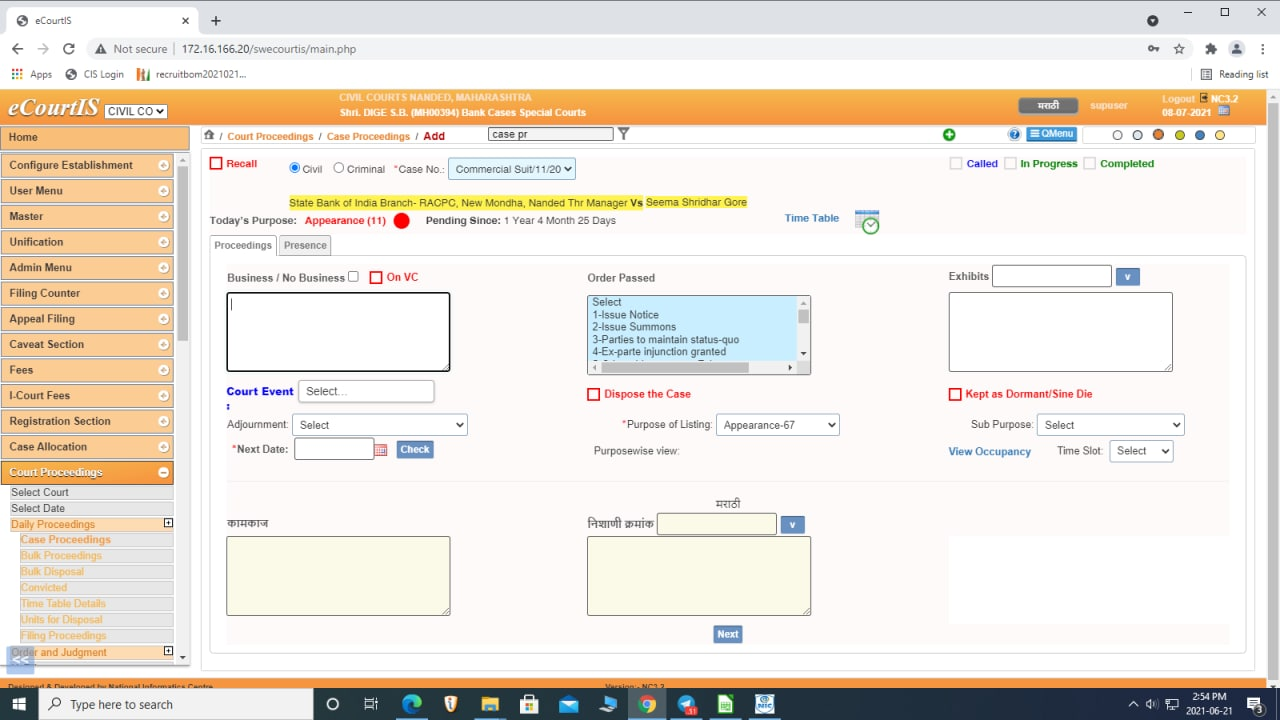
If a case is listed on the same stage on next date, the indicator depicts as follows:
Along with the coloured indicator, number of times the case is listed on the same stage along with period/time since when the case is listed on the same stage is also shown. The alert assists the Judges to decide in adjourning the cases further on the same stage or to list for next stage.


• The Case Information Software 3.0 was launched on 14.08.2018 to transform the judicial system of the country by Information Communication Technology (ICT) enablement of Courts.
• In order to enhance judicial and court productivity, “Electronic Case Management Tools (ECMTs)” has been introduced for judges and lawyers which can be accessed from both eCourt Services web portal and mobile application anywhere and anytime.
• The ECMTs have integrated India Code with more than 800 laws and regulations, 25 advocate forms and e-filing portal link all in one place.
• Integration of Electronic Case Management Tools in one digital platform has been completed which is a key reform under Enforcing Contracts.
Electronic Case Management Tools (ECMTs) For Judges
• The JustIS app for Judicial Officers integrating 8 Electronic Case Management Tools (ECMTs) was launched on 04.01.2019.
•All 8 Electronic Case Management Tools are available to Judicial Officers through JustIS app and Case Information System 3.2 software:
i. Access laws, regulations and case law;
ii. Automatically generate a hearing schedule for all cases on their docket
iii. Send notifications to lawyers
iv. Track the status of a case on their docket
v. View & manage case document
vi. Assist in judgment writing
vii. Semi-automatic generation of court orders
viii. View court orders and judgments in a particular case.

• Through this app the judge can see only the data pertaining to his court. Upon transfer the JO Court of the new officer is tagged to the Court and he starts seeing the data.
• Currently, more than 18,846 Judicial Officers (as on 30.04.2023) have downloaded the JustIS App (Android and iOS versions) that has all the 8 ECMTs integrated in one single portal.
• Recently, the eCommittee of Supreme Court of India has made JustIS Mobile App for Judicial Officers available on iOS and Android platforms.
Electronic Case Management Tools (ECMTs) For Lawyers

• All 7 Electronic Case Management Tools for lawyers are integrated in one single portal and the same is available at ecourts.gov.in and eCourts services mobile app which is integrated with CIS 3.2 software.
• Following 7 eCMTs are integrated on www.ecourts.gov.in:
i. To access laws regulations and case laws and integration with India Code Portal.
ii. To receive notifications-eMails.
iii. To access forms to be submitted to the court.
iv. To track the status of a case.
v. To view and manage case documents.
vi. To file briefs and documents with the court.
vii. To view court orders and decisions in a particular case.


• Currently, there are 1.79 Crores Lawyers ( as on 30.04.2023) using the Electronic Case Management Tools. The App can be downloaded using the links :
• Recently, the e-Committee, Supreme Court of India has issued user friendly manual for e-Courts Services Mobile Application and uploaded it on the official website of e-Committee in 14 different languages namely English, Hindi, Assamese, Bengali, Gujarati, Kannada, Khasi, Malayalam, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Telugu, Punjabi and Tamil.
Click here for Manual on e-Courts Services Mobile Application in various languages







The introduction of The Commercial Courts (Amendment) Act, 2018 and Rules ushered in “Pre-institution Mediation and Settlement” of commercial cases.
Pre-Institution Mediation and Settlement (PIMS) mechanism, with opt out option, was introduced to reduce pendency of cases and to promote mediation as a viable dispute resolution alternative in commercial cases.
This pioneering initiative of alternative dispute resolution mechanism has led to dispute avoidance, reduced clogging of cases in commercial courts and made enforcing contracts easier. Further, to facilitate institutional mediation & arbitration, various High Courts have provided for Mediation and Arbitration centres annexed to the Commercial Courts. Other HCs are facilitating commercial mediation through ADR/Mediation Centres run by the Legal Services Authority.
The Department of Justice hosts an online portal for reporting of information from all High Courts regarding the Mediation and Arbitration centres annexed to the Commercial Courts on its website.
Link to Arbitration and Mediation portal
Committee on Simplification of Rules and Forms:
The Department of Justice has constituted the Committee to work on simplification of Rules and Forms relating to Pre-Institution Mediation and Settlement and to examine the overall functioning of the Pre-Institution Mediation system including rationalization of Mediation fees. The composition of this Committee includes Registrar Generals from the High Courts of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka and Department of Legal Affairs.

• Prime Minister Modi has emphasized that “Digital India guarantees transparency, effective service delivery and good governance”. In sync with his thinking, galvanized efforts were made to introduce “e-Filing Facility” in all the Dedicated Commercial Courts from 2018.
• e-filing system enables electronic filing of legal papers. Using e-filing, cases (both civil and criminal) can be filed before the High Courts and District Courts that have adopted e-filing systems. Introduction of e-filing is aimed at promoting paperless filing and saving time and cost by adopting technological solutions to file cases before courts in India.

• E-filing has been made mandatory for all the Central Government Ministries/Departments in commercial litigation. Further, state of Karnataka and Delhi have also made e-filing mandatory for all government commercial litigation. Besides reducing cumbersome procedure and logistical inconvenience, paperless filing coupled with “e-summons” facility has led to time and cost saving efficiencies.
• e-Committee has launched 3.0. version of e-Filing in Commercial Courts which is robust, upgraded and user-friendly with new advanced features.
• E-Committee, Supreme Court of India is also working on the paperless digital court pilot project. Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, Madhya Pradesh and Kolkata have been selected for the paperless digital court pilot project. The pilot project will be launched soon.
Delivery of summons to parties to a litigation have been a perennial problem for courts in India which face a daunting task of clearing a backlog of around three crore cases at various levels across the country.
The service of summons and processes by traditional methods are often a cause for inevitable delay in speedy disposal of cases. National Service and Tracking of Electronic Processes (NSTEP) is a centralised process service tracking application comprising of a web application and a complementary mobile app designed to streamline the process. NSTEP Mobile App provided to bailiffs and process servers enable transparent tracking of service of notices and summons in real-time.
Once the process is adopted through CIS software by the respective courts, it will become available on the NSTEP web application in the electronic format. NSTEP web application enables allocation of published processes to bailiffs if service is to be effected within their jurisdiction. It also facilitates allocation of published processes to respective court establishments inter-district or inter-state.
Legal enactments:
• Order V, Rule 9 of the Code of Civil Procedure, 1908 specifies that summons may be served either by speed post or courier service or by any other means of transmission of document (including fax or electronic mail service).
• Delhi has notified Delhi Courts Service of Processes by Courier, Fax and Electronic Mail Service (Civil Proceedings) Rules, 2010 on 09.02.2011.
• Mumbai has notified Bombay High Court Service of Processes by Electronic Mail Services (Civil Proceedings) Rules, 2017 on 03.05.2019.
Committee on e-Summons
One of the impediments faced by the Commercial Courts while serving eSummons was the lack of data of Companies/Directors that are party to a commercial litigation. This resulted in delay in the serving of eSummons thereby increasing the time taken for trial and judgment of a commercial dispute. To address this issue, Department of Justice constituted a Committee on eSummons on 03.11.2020 with members from Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Registrar of Companies, NIC, eCommittee and Registrar Generals of High Court of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka to facilitate sending online summons through emails and SMS alert by obtaining database of companies registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
The Committee has developed software patch for consuming database of companies registered with the MCA and it has been provided to the Commercial Courts in Mumbai, Delhi and Bengaluru city to facilitate sending of online summons to commercial disputes. Once testing is completed, it will soon be implemented across the Commercial Courts making the electronic service of processes and serving of eSummons more seamless, effective and efficient.
To improve the functioning of the Commercial Courts and overall contract enforcement regime in India, Department of Justice in collaboration with other stakeholders has constituted various committees and sub-committees comprising of bureaucrats, lawyers, experts, academicians, professionals, etc. The suggestions and inputs received from these committees have made the enforcement of contracts in India more effective, efficient and expeditious.
Committee On e-Summons:
One of the impediments faced by the Commercial Courts while serving eSummons was the lack of data of Companies/Directors that are party to a commercial litigation. This resulted in delay in the serving of eSummons thereby increasing the time taken for trial and judgment of a commercial dispute. To address this issue, Department of Justice constituted a Committee on eSummons on 03.11.2020 with members from Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Registrar of Companies, NIC, eCommittee and Registrar Generals of High Court of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka to facilitate sending online summons through emails and SMS alert by obtaining database of companies registered with the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (MCA).
The committee has developed the software patch for consuming database of companies registered with the MCA and it has been provided to the commercial courts in Mumbai and Delhi to facilitate sending of online summons in commercial disputes. Once testing is completed, it will soon be implemented across the Commercial Courts making the electronic service of processes and serving of eSummons more seamless, effective and efficient.
Committee On Simplification Of Forms And Rules:
The Department of Justice has constituted a Committee on Simplification of Rules, Forms and Pre-Institution Mediation and Settlement (PIMS) Rules, following the directions from the Cabinet Secretary regarding implementation of efforts required to reduce the compliance burden for citizens and business activities. The composition of this Committee includes Registrar Generals from the High Courts of Delhi, Bombay, Calcutta and Karnataka and Department of Legal Affairs.
The Committee has been assigned to work on simplification of Rules and Forms relating to Pre-Institution Mediation and Settlement and to examine the overall functioning of the Pre-Institution Mediation system including rationalization of Mediation fees. The said Committee is also tasked to prepare the draft Commercial Court Rules as per Section 21A(2)(b) of the Commercial Courts Act, 2015.
The core group of the Committee has finalised the Commercial Court Rules, 2021 as per Section 21A (2) (b) of the Commercial Courts Act, 2015 and the same is under examination of the Department of Legal Affairs.
Committee On Linkage Of Property Registration With Court Proceedings:
Department of Land Resources has constituted a committee for linkage of property registration with court proceedings by drafting standard operating procedures and to launch pilot project. The Committee comprises members from Department of Land Resources, Department of Justice, eCommittee, NIC and Revenue Departments of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra.
The Committee constituted for linking of e-Court with land records and registration database through APIs in its meeting held on 04th December, 2020 had decided that the Revenue Departments of Government of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh and Maharashtra would share their data with the e-Courts team APIs so that the pilot testing can be conducted in these three States to start with the scheme of things. The pilot project has been tested successfully in Uttar Pradesh, Haryana and Maharashtra. Soon it will launched across the country.
Steps are being undertaken to facilitate the State Governments in getting necessary clearances for finalising the nationwide launch of linking of e-Court with land records and registration database.
Committee with Law Firms:
Department of Justice in coordination with Invest India had constituted three Sub-Committees with representatives from top Law Firms from India for suggesting reforms pertaining to the improvment of the functioning of Commercial Courts in India, particularly in Delhi and Mumbai. The sub-committees had to suggest reforms on the following aspects:
• Time Standards and Delays
• Pre-Institution Mediation & Settlement and
• eCourt services.
The sub-committees had submitted their suggestions that had been duly forwarded to the concerned authorities for necessary action.
Other Major Reforms Undertaken
I. Special Courts for Infrastructure Project Contracts: 23 High Courts have set up designated Special Courts for Infrastructure project contracts disputes as per Section 20B of the Specific Relief (Amendment) Act, 2018. Further, High Courts of Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Allahabad and Calcutta have allocated dedicated days in a week/month for hearing of such disputes related to infrastructure project contracts.
II. Special Benches for high value commercial disputes: High Court of Delhi, Orissa, Andhra Pradesh, Allahabad, Jammu & Kashmir, Sikkim, Patna and Madras have set up Special Benches for dealing with high value commercial disputes i.e. above Rs. 500 crores. Other High Courts are also considering the proposal.
III. Bombay and Delhi HC have set up courts for high value commercial disputes i.e. above Rs. 100 crores.
IV. Establishment of Dedicated Commercial Courts across the country: To provide conducive environment for speedy resolution of commercial disputes and for attracting global investments various High Courts have set up Dedicated Commercial Courts under their jurisdiction. At present, 14 High Courts have set up such Dedicated Commercial Courts to facilitate hassle free adjudicatory mechanism for both lawyers and litigants.
V. Specialised online course on Business and Commercial Laws: A three-month online certificate course on Business and Commercial Laws has been launched in collaboration with National Law University, Delhi which has been specifically designed for lawyers, company secretaries and chartered accountants for familiarizing them with commercial law, procedures and eCourt Service.

VI. Commercial Court Guide: Commercial Court guide being prepared by National Law University, Delhi.
a) 3 Webinars were organized by the Department of Justice with the Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) for commercial lawyers from Delhi, Mumbai and South Indian metro cities on reforms implemented under Enforcing Contracts Indicator.

b) National Webinar was organized on 19.09.2020 by the Department of Justice in conjuction with Invest India and commercial law firms of Delhi on reforms implemented under Enforcing Contracts Indicator. Subsequently, 3 Sub-Committees were formed to seek suggestions.

c) Webinar was organized on 10.10.2020 by the Department of Justice with ASSOCHAM on reforms implemented under Enforcing Contracts Indicator for corporate firms and lawyers.
Youtube Video : Webinar on Reforms Implemented under Enforcing Contracts Indicator